This tool version is unpublished and cannot be run. If you would like to have this version staged, you can put a request through HUB Support.
SIMPLE-G
SIMPLE-G
Launch Tool
Archive Version 1.0
Published on 08 May 2017
Latest version: 1.1.1.7. All versions
This tool is closed source.
Category
Published on
Abstract
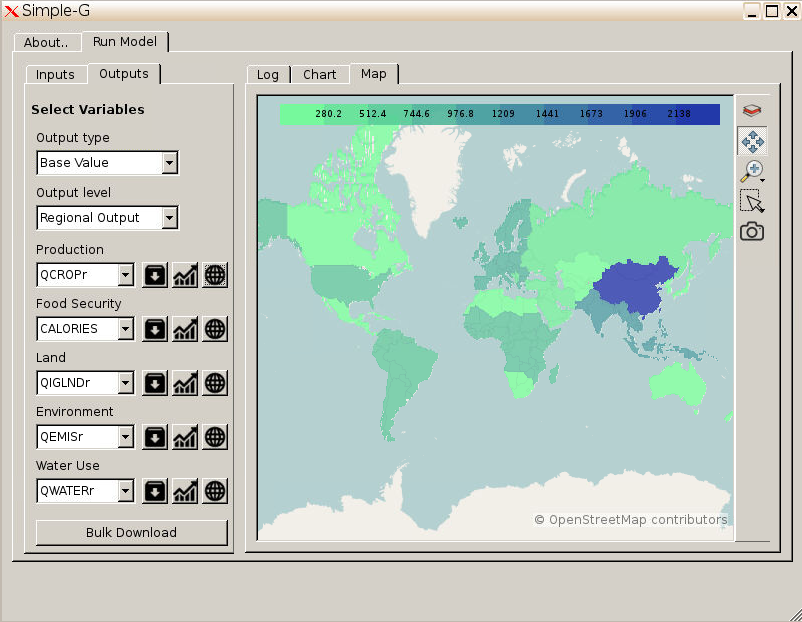
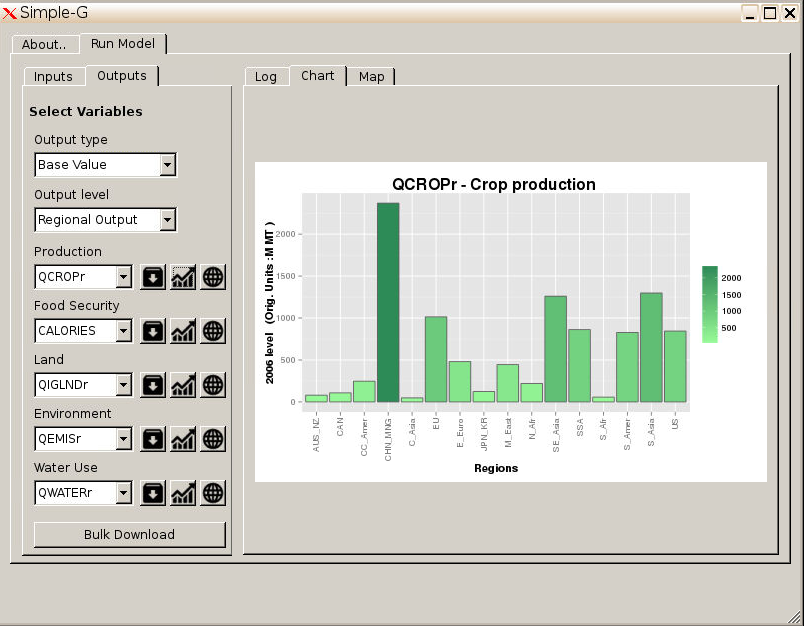
SIMPLE-on-a-Grid (SIMPLE-G) is a multi-region, partial equilibrium model of gridded cropland use, crop production, consumption and trade. It is an extension of the SIMPLE model that has been applied to study long run sustainability issues in the global food-water-environment nexus. Rather than looking at regions or country aggregates, SIMPLE-G divides the world into georeferenced grid-cell units. This allows SIMPLE-G to explicitly incorporate local environmental constraints in its projections, account for sub-national heterogeneity of global drivers such as climate change and water scarcity, and assess local land and water use given future trends the global farm and food system.
In SIMPLE, the world is split into sixteen economic regions. Regional consumption is disaggregated into four commodities (crops, livestock, processed foods and biofuels). Regional demand is driven by population, per capita income, and biofuel mandates (all exogenous in the model) as well as prices (endogenous to the model). SIMPLE-G extends the existing SIMPLE model by disaggregating rainfed and irrigated production and modeling these processes at the individual grid-cell level. Regional crop output is obtained by aggregating across the grid cells (30 arc-min resolution) within each region. Crop production follows a nested constant elasticity of substitution (CES) function. Water is an explicit input used by the irrigated sector only. Water consumption is computed as the product of gridded irrigated cropland area and a grid cell-specific consumptive water use parameter in m3/ha. By aggregating water use across grid cells within a sub-basin (defined below), we obtain total irrigation consumption. Water availability at each grid cell is exogenous in SIMPLE-on-a-Grid, and is obtained from the hydrological model.
Credits
This web-app version of SIMPLE-G is based on key experiments from Liu et al (2017). “Achieving Sustainable Irrigation Water Withdrawals: Global Impacts on Food Production and Land Use.” In prep. This app also considers alternative growth rates for the following model drivers for the period 2006-2050.
- Population and Income Growth : Shared Socioeconomic Pathways SSP1 to SSP5 (v. 0.9) (see O’Neill et al 2015, Global Environmental Change vol. 42)
- Global Demand for Biofuels: Current Policies, New Policies 450 Policies from IEA's World Energy Outlook (2008,2012)
- Agricultural Productivity Growth: Historical Growth, Low Growth, High Growth using adjusted estimates from USDA-ERS (see https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/international-agricultural-productivity/)
- Livestock Productivity Growth: Historical Growth, Low Growth, High Growth using adjusted estimates from Ludena et al. (2007) Agricultural Economics 37
References
J Liu, T Hertel, R Lammers, A Prusevich, U Baldos, D Grogan, S Frolking.(2017) Achieving Sustainable Irrigation Water Withdrawals: Global Impacts on Food Production and Land Use. Environmental Research Letters (in review )
Graphical user interface was created by:
Jaewoo Shin
Citations
Shin, Baldos, Zhao (2017) SIMPLE-G Web App (v1.0)
Cite this work
Researchers should cite this work as follows: